By Tanay Kanungo

As global temperatures rise and the demand for cooling increases, it is crucial to find sustainable cooling solutions to mitigate the impact of climate change. This blog will explore the importance of sustainable cooling and discuss some potential solutions to this critical issue.
The world's population is growing, and so is the demand for cooling. But did you know that conventional cooling technologies are contributing to the very problem they're trying to solve? Yes, most of the traditional cooling is directly contributing to global warming. It's time to rethink our approach to cooling and embrace sustainable solutions that can help us stay cool without harming the environment. Sustainable cooling is essential for mitigating climate change, improving energy efficiency, and promoting social equity. By adopting innovative technologies and supporting policy initiatives, we can transition to a greener future where cooling is accessible, efficient, and environmentally friendly.

Green Heating & Cooling: How Can I Make My HVAC More Sustainable?
The Growing Demand for Cooling
As highlighted in the paper "Cooling for sustainable development"[1], the demand for cooling systems is rapidly increasing due to population growth, urbanization, and rising global temperatures. A very good example of the growing demand for cooling is the developing country of India, where more and more people can now afford appliances like Air Conditioners and refrigerators as a huge chunk of low-income population move into the middle income segment. As more and more population move in the middle income segment. The global cooling demand growth is almost 3 times that of the global GDP growth. This surge in demand has significant implications for energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and social equity.
The Environmental Impact of Conventional Cooling
Traditional cooling systems rely on hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which are potent greenhouse gases. The paper "Potentials of GHG emission reductions from cold chain systems: Case studies of China and the United States" emphasizes the need to reduce HFC emissions from cooling systems to mitigate climate change. In addition to traditional refrigerants contributing to global warming, increased energy consumption due to surging cooling demand is met by burning fossil fuels, which further worsens cooling’s role in climate change.
Sustainable Cooling Solutions
To address the environmental and social challenges posed by conventional cooling, we must embrace sustainable cooling technologies. Some innovative solutions include:
- Passive Cooling: Harnessing natural processes to cool buildings without energy-intensive air conditioning systems, such as green roofs and natural ventilation. This additionally removes the need to use mechanical cooling. This could greatly benefit off-grid locations.
- Solar-Powered Cooling: Using the sun's energy to power air conditioning and refrigeration units, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions.
- District Cooling: Providing centralized cooling for multiple buildings in which chilled water travels from the plant to the building, cooling the space, and returns to the plant to be cooled again, improving energy efficiency and reducing the need for individual air conditioning units.
- Advanced Refrigerants: Developing new refrigerants with lower global warming potential (GWP) than traditional HFCs, reducing the environmental impact of cooling systems while maintaining or improving their performance. Examples of low GWP refrigerants are carbon dioxide, ammonia, hydrocarbons, HFOs such as R-1234yf, R-1234ze and R1233zd.
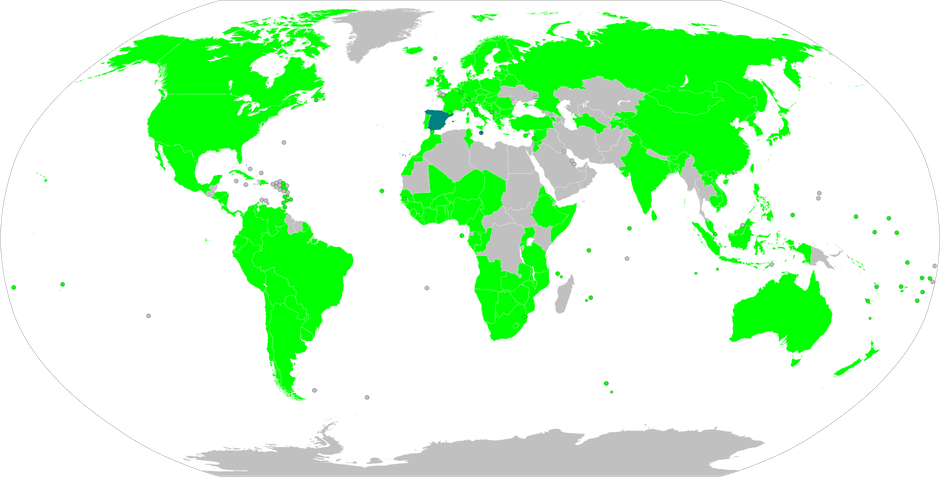
Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol Ratification map.svg - Wikimedia Commons.
The Role of Policy and Collaboration
To accelerate the transition to sustainable cooling, we must support policy initiatives and foster collaboration. Some key actions include:
- Phasing Out HFCs: The Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol aims to phase down the production and consumption of HFCs, since 1987, all 197 member states of the United Nations, among others, have ratified the Protocol. Demonstrating the global commitment to sustainable cooling. HFCs have since largely replaced CFCs
- Local Government Support: Governments can incorporate sustainable cooling in their climate pledges (nationally determined contributions) and ensure that sustainable cooling considerations are included in energy, urban, transport, agricultural and health service projects, among others. On the supply side, governments can act swiftly to encourage manufacturers to improve the energy efficiency of their cooling products and to lower the global warming potential of refrigerants.
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of sustainable cooling and the available solutions is crucial to driving change and encouraging adoption. Schools and other educational institutions need to include sustainable cooling in their curriculum to shed light on this widely avoided problem and its solutions.
In conclusion, embracing sustainable cooling is vital for combating climate change and promoting a greener future. By adopting innovative technologies, supporting policy initiatives, and raising awareness, we can transition to a world where cooling is accessible, efficient, and environmentally friendly. As responsible human beings, it's our responsibility to champion sustainable cooling solutions and work together to ensure a cooler, greener planet for generations to come.
Kommentar schreiben